Laparoscopic Hernia surgery
What is hernia?
The abdominal muscles do a good job of protecting internal organs and keeping them in place. But sometimes muscles can tear or weaken, allowing an organ or fatty tissue to push (or herniate) into an area where it doesn’t belong.
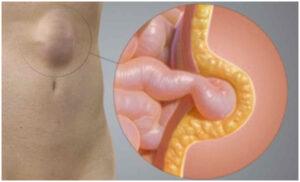 | When that happens you might notice a lump or bulge, although sometimes these protrusions can’t be felt. Other times, the bulge might come and go, depending on your position or what you’re doing. These weakening’s in the muscle wall and the subsequent tissue or organs that push through are called hernias. |
What are the types of hernia?
Most hernias occur in the abdominal area, between your chest and hip bones. Hernias that can be pushed back into place are called reducible hernias. Those that can’t be pushed back into position are termed irreducible or incarcerated.
Most common hernias
| Hernias are further classified by the body region where they occur. Some of the more common ones include: | 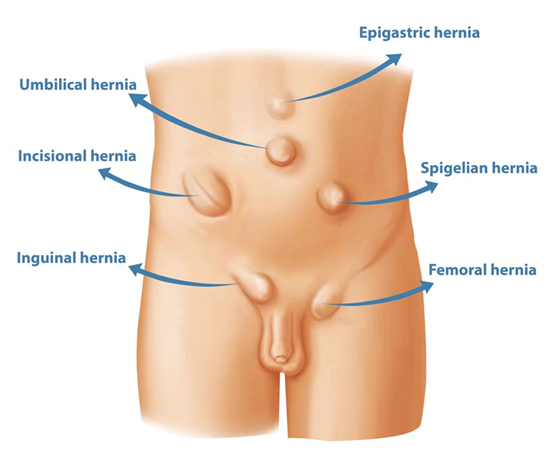 |
Inguinal hernias: These typically occur in the inguinal canals, which are located on either side of the groin. Inguinal hernias are one of the most common types of hernia, affecting 27% of men and 3% of women.
Umbilical hernias: These occur when tissue or parts of the intestine push through a weak area near the navel. They account for 6-14% of adult abdominal hernias, making them the second most common type. Up to 20% of newborns have this hernia. If not closed by age 5, it needs to be closed surgically.
Hiatal hernias: These occur when parts of the stomach or other organs break through an opening in the diaphragm. Hiatal hernias are very common and the overwhelming majority are what’s known as “sliding” hiatal hernias, meaning they can move in and out of place.
Femoral hernias: These are found in the lower groin area, near the upper thigh. Because of their wider pelvises, women are four times more likely to develop femoral hernias than men.
Incisional hernias: The cutting and sewing of surgery can weaken a muscle wall, making it more likely a hernia will develop. Roughly 15% of people will develop an incisional hernia after surgery involving the abdominal wall.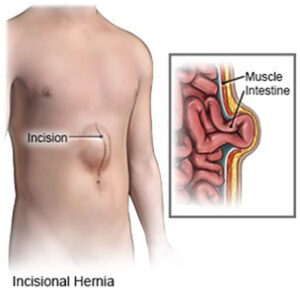
Because Bariatric surgery is used to treat metabolic conditions like Type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypercholesterolemia etc..
What are the Hernia Symptoms?
You might notice a bump or bulge (it may be hard or soft) in and around abdomen. Swelling might come and go, usually size increases on straining and coughing, reduces on lying down position. Not all hernias produce discomfort, but when they do you might experience:
- • Burning
- • Pulling
- • Pain
- • Pressure
- • Swelling
- • Digestive issues like heartburn or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
The discomfort may be more intense when you strain (for example, while having a bowel movement or lifting a heavy object) or tighten your abdominal muscles (when you’re coughing, sneezing or exercising, for instance).
How to Diagnose or detect hernia?
Your doctor will perform a physical exam, feeling for a hernia while you sit, stand or even cough. Imaging tests like an ultrasound or computerized tomography (CT) scan may also be ordered.
What is the Treatment of hernia?
How your hernia is treated depends on a number of factors, including where the hernia is located, its size, whether it’s growing and if it’s causing you discomfort.
Surgery
In general, For hernias that are large, causing pain or impacting your quality of life, surgery may be recommended. Types of hernia surgery include open surgery, laparoscopic surgery.
Open Surgery
In open surgery, the surgeon cuts through the body where the hernia is located. The bulging parts are put back into place and the tear is stitched.
Instead of sutures, a doctor might use a mesh panel (usually made of plastic or animal tissues) to provide added support. Those who have their inguinal and femoral hernias repaired with a mesh appear to have a reduced risk of hernia recurrence.

What is laparoscopic Hernia Surgery?
Using small incisions through which surgical tools (usually a flexible tube with a camera and light that guides the surgeon), the organs/tissues are moved back to where they belong and the hole is repaired. This is considered minimally invasive surgery and has a quicker recovery time than open surgery.
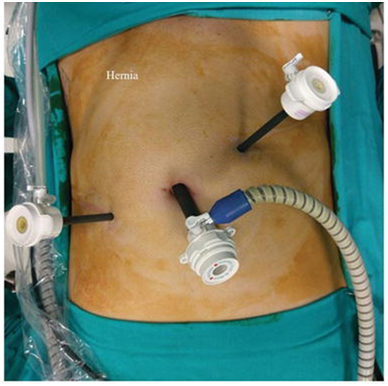
What are the Advantages of laparoscopic hernia surgery?
1. Smaller Incisions with better cosmetic result
2. Reduced post-operative pain, swelling and discomfort
3. Faster recovery
4. Faster return to work and activity
5. Reduced incidence of wound healing complications (i.e. infection and wound separation)
6. The ability to perform additional intra-abdominal procedures at the same time
7. Increased ability to diagnose and repair additional asymptomatic hernia defects. During minimally invasive surgery the opposite side can be clearly visualized. In this manner, both sides can be repaired with no need for additional incisions. Since 30 % of patients with groin hernias will have an asymptomatic hernia on the opposite side, the minimally invasive technique for hernia repair has a significant advantage in this respect. the occult hernia consisted of a beginning hernia. Eventually, one of five will become symptomatic and require repair. These outcomes support immediate repair of occult defects, no matter its size
What are the Potential Risks of Hernia Repair Surgery?
The main risks of hernia repair surgery include:
• Bleeding or hematoma – when blood collects under the surgical site.
• Seroma – fluid collection under the surgical site.
• Infection, potentially of the surgical site or the surgical mesh used for repair.
• Chronic postoperative pain.
• Bowel or urination issues such as constipation or trouble urinating.
• Nerve or tissue injury or damage.
• Hernia recurrence.
How it works: This procedure involves creating a small stomach pouch. This reduces the amount of food you can eat. The intestine is connected to the new pouch and rerouted. The pouch is connected directly to the lower part of the small intestine. Food bypasses the lower stomach, the first part of the small intestine (duodenum) and some of the second part (jejunum). The changes created during gastric bypass cause changes in the way the gut and the pancreas interact. This affects diabetes control even before weight is lost. Patients generally can return to work within three to four weeks. Gastric bypass is a good surgical option in many patients.
How long I can wait to get hernia surgery after diagnosing one?
Its always better to get the hernia surgery done as early as possible, before patient develops complications of hernia. According to few guidelines its better to get the surgery done within one month of diagnosing hernia.
What happens if a hernia is left untreated?
A hernia will not heal on its own. Left untreated, a hernia will become larger and can cause serious health problems. Intestine may get trapped in the hernia and become trapped or incarcerated. It may become strangulated by cutting off blood flow to the trapped tissue. This can be a life-threatening emergency.
What is the Recovering time from Hernia Repair Surgery?
Recovery time for hernia repair surgery varies depending on what kind of surgery you had. For laparoscopic surgery, it’s typically about one to two weeks. For open repair surgery, it’s usually about three weeks. Patient should abstain from doing straineous work and lifting weights of more than 5kgs for about 4weeks after laparoscopic surgery and for about 6weeks after open surgery.
What is hernia mesh?
A hernia mesh serves as a flexible scaffold in hernia repair surgery. It has the ability to reinforce the muscle walls and also prevent the organs from coming through. As such, it prevents the patient’s condition from worsening.As per several studies, a surgical mesh can reduce the rate at which hernia can re-occur.
During the hernia surgery, the surgeon places the mesh on top of the open hernia. The surgeon also uses additional medical devices such as tacks, sutures, and surgical glue to hold the surgical mesh in its place. As time goes by, the patient’s tissue typically begins to grow into the small pores present in the mesh, while also strengthening the muscle wall. This condition creates scar tissues, which strengthen the site of the hernia. The mesh repairs made during a hernia mesh surgery are usually permanent, which means that the implant remains fixed in the patients’ body for the rest of their life.
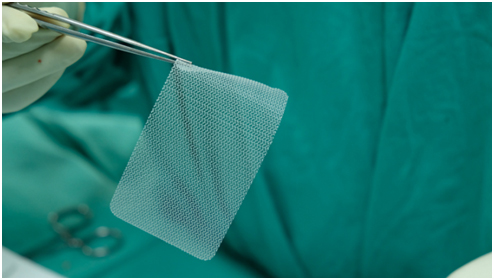
What are the types of hernia mesh?
